INTRODUCTION

DEF: The mandible or inferior maxillary bone is the largest, strongest, and lower bone is the largest, strongest, and lowest bone in the face.
It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place.
It comprises of Body, Ramus, Angle, Condylar process, and coronoid process.
Parts of the mandible:

Osteology:
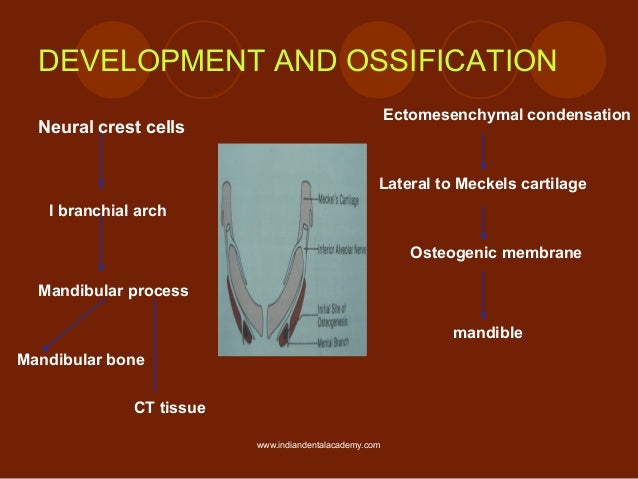
- The mandible is the SECOND BONE after clavicle to ossify in the body
- Parts that are ossified are INCISIVE PART
- The upper half of the ramus
- Each half of mandible ossifies from one center which appears in the 6TH WEEK OF INTRAUTERINE LIFE in the mesenchymal sheath of meckles cartilage(near mandibular nerve).
- Ossification stops at one point and its later called MANDIBULAR LINGULA.

The endochondral ossification
It can be seen in 3 areas,
- The condylar process -14th week
- The coronoid process- 10-14 week of IU life
- The Mental region - 7th month of IU life
The Body
- Horseshoe-shaped
- Has two surfaces and two borders
- surfaces: External and Internal
- Borders: upper and lower
Features
- Outer surface
- Symphysis menti
- Mental protuberance
- Mental tubercules
- Mental foramen
- Oblique line
- Incisive fossa
2.Inner surface
- Genial tubercles
- Mylohyoid line
- Submandibular fossa
- Sublingual fossa
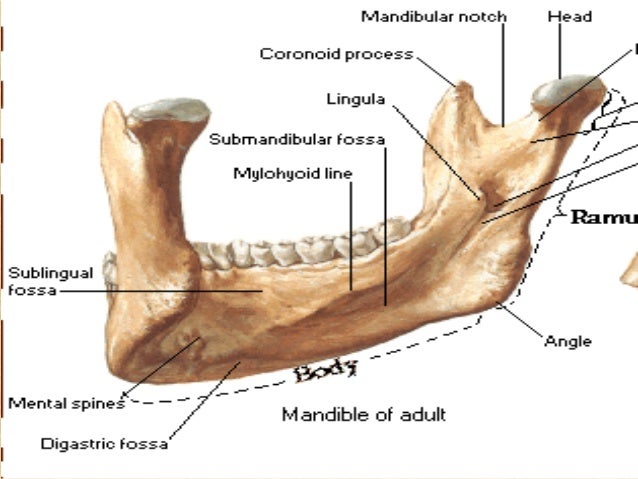
Upper border or alveolar part
It contains 16 alveoli for the roots of teeth, varying in size and depth, some being multiple.
Lower border or base
Near the midline, The base shows an oval depression called DIGASTRIC FOSSA.
The ramus
- Quadrilateral in shape
- consists of two surfaces, four borders, and two processes.
- Two surface-Lateral, Medial
- Four borders- Upper, lower, Anterior, Posterior
- Two processes- Coronoid, condyloid
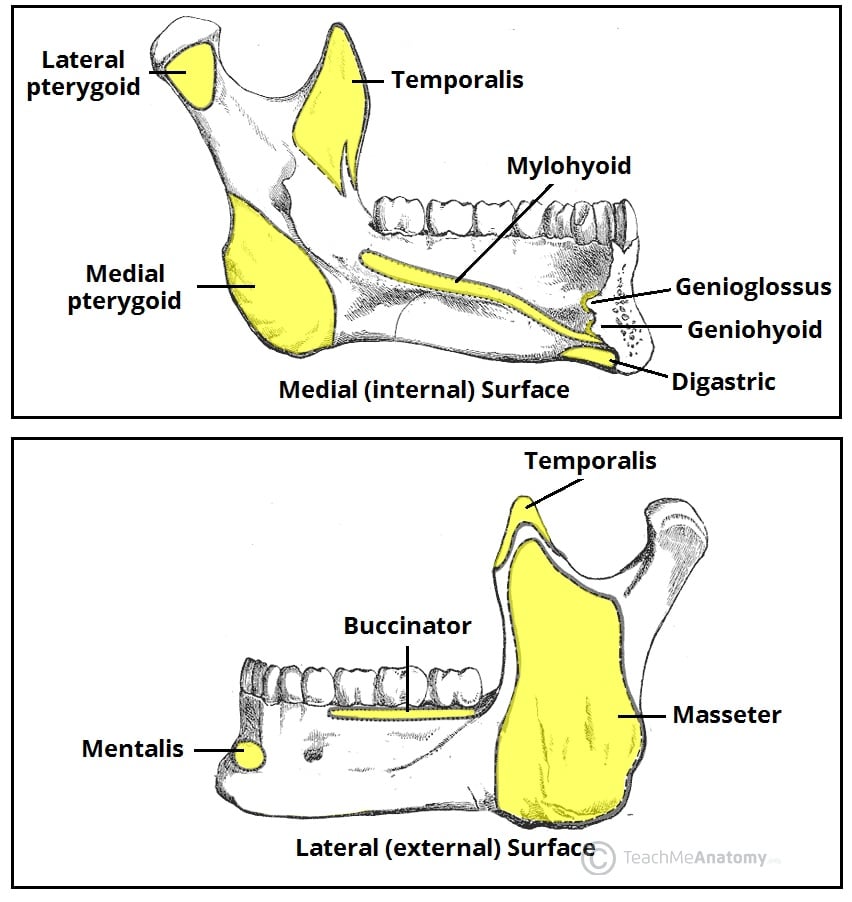
ATTACHMENTS
1.on lateral surface
- Oblique line- Buccinator
- Incisive fossa- origins to Mentalis and orbicularis oris
- Insertion to masseter
- Posterosuperior part: Parotid gland
- Lateral ligament of TMJ
- The mucous membrane of the mouth
- Platysma is inserted
- Deep cervical fascia

2.On medial surface
- Digastric fossa-Anterior belly of digastric
- Genial tubercles-Genioglossus and geniohyoid
- Mylohyoid line-mylohyoid muscle
- Pterygomandibular raphe- superior constrictor
- Sphenomandibular ligament-lingula
- pterygoid fovea-lateral pterygoid
Foramina
1.Mental foramen- mental nerve and vessels
2.Mandibular foramen-Inferior alveolar nerve and vessels
Blood supply
1.Inferior alveolar artery
2.Periosteum
Nerve supply
1.Long buccal nerve
2.Inferior alveolar nerve
3.Lingual nerve
Lymphatic drainage
1.submandibular group of lymph nodes
2.submental group of lymph nodes
3.Deep cervical lymph nodes
Thank you for reading
We are just trying to help dental students. These are all just the important points to be remembered.
Any questions, doubts, or any topic suggestions can be placed in comments, mail us in dental.champ@gmail.com, or ping us in Facebook- dental champ and on Instagram- dental_champ.
Comments
Post a Comment